Metal forming :Hot die forging
At present,Weforging Manufacturing Company has 6 sets of 400T-1000T-1600T-2500T-4000T hot die forging presses,10 sets of 63T-125T-315T-400T-630T-800T-1000T-1250T closed type presses,2 CNC ring forging machines and 4 oil presses. Mainly with hot die forging;25T-40T-63T-200T-630T-800T forging hydraulic press, mainly used for cold extrusion and nut forging.
The forging base has a total of 20,000 square meters, and the cutting machine is used in the whole process.
The production line is heated by infrared temperature-controlled IGBT induction heating furnace, with an annual capacity of 30,000 tons.

Current machining equipment in Weforging:
The main types of hot forgings are shaft, gear, cylinder, disk and special-shaped. Involved in mining machinery parts, Marine forgings, energy forgings, agricultural machinery, forestry machinery, engineering machinery, engines and other mechanical equipment construction field, weight in 0.01-1000kg. The precision reaches the international advanced standard of hot precision forging.

Laboratory:
Mechanical properties Lab three
Mitoyo three coordinate measuring room
Gear measuring room
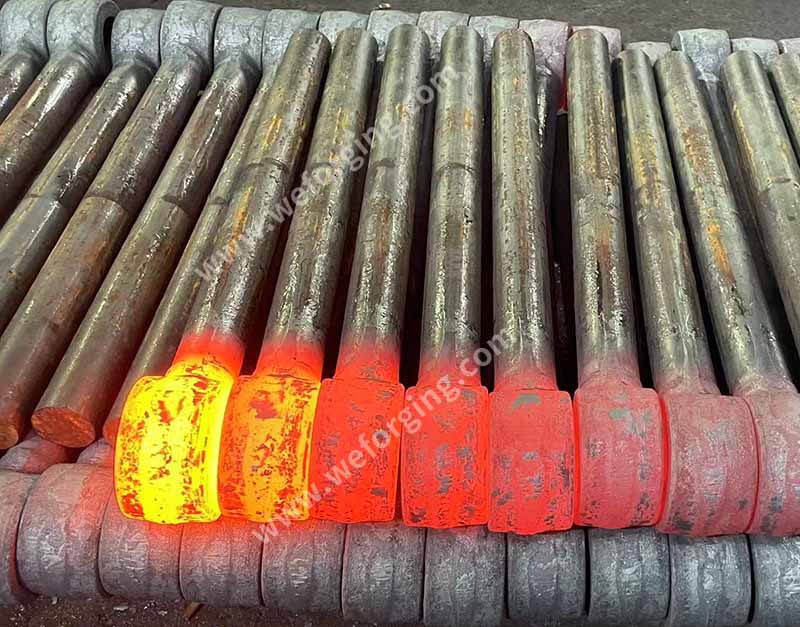


Why hot forging
Forging is a kind of metal forming technology, which is widely used in gear and other mechanical fields requiring high safety performance.
Hot die forging is a way of forging, usually refers to the rod by heating to a higher temperature than the recrystallization of the material,and in a certain mold cavity, through the pressure forging equipment, so that the metal flow in the mold cavity, and plastic forming into the shape and size required for forging, and finally cutting, punching and correction.
Hot die forging and free forging
Hot die forging:
Suitable for certain shape, high precision, mass production;
The mold cost is high, but the single cost is low and efficient;
Temperature controllable, relatively stable quality, suitable for mass production;
Free forging:
Suitable for forging of large/heavy parts (Marine drive shaft).
Simple mold cost is low, but the material waste is large, and is not conducive to subsequent machining.
Suitable for small batch customization or trial production stage verification;
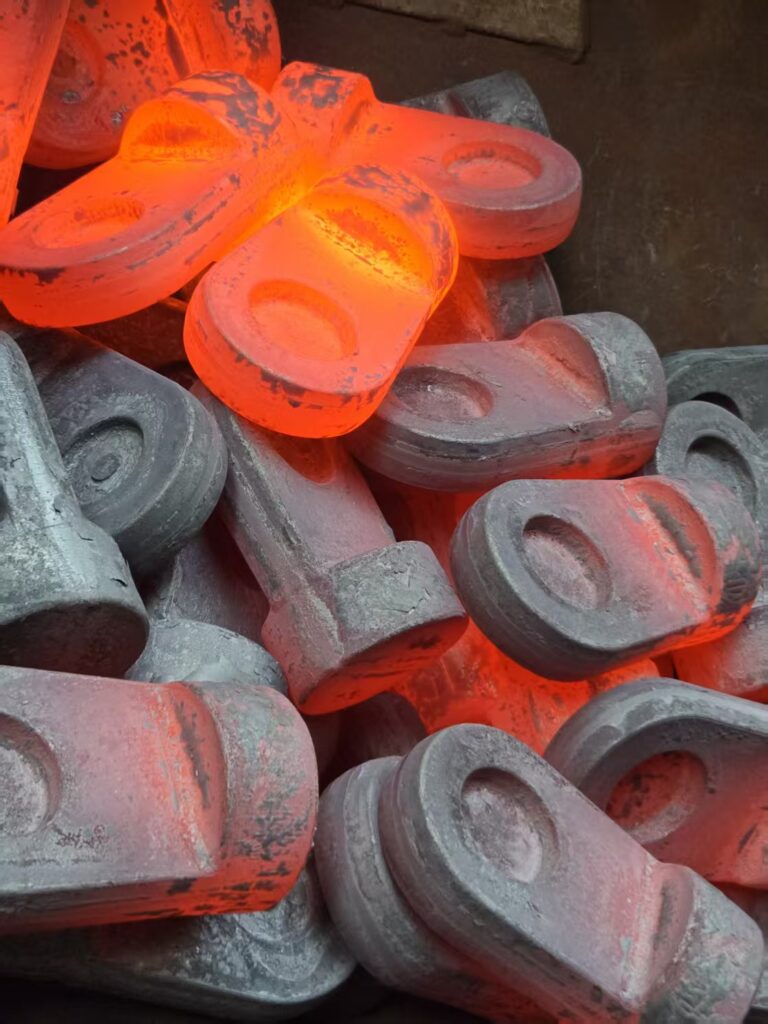

Forging forming and testing process flow:
(1) Cutting
Blanking: Cutting raw materials (bars, ingots, etc.) into billets of the desired size.
(2) Heating and pre-forging (preforming)
Heating: the billet is heated above the recrystallization temperature (such as carbon steel is usually 1100~1250 ° C) to improve metal plasticity and reduce deformation resistance.
The initial forming on the free forging or coarse die forging equipment can reduce the metal flow resistance during the final forging and improve the die life.
Common methods: roll forging, upsetting, drawing and so on.
(3) Final forging (die forging forming)
The pre-forged blank is placed in a precision matched upper and lower die and formed under the action of a press or forging hammer.
(4) Trimming and punching
Trimming: Remove the flash around the forging.
Punching: If the forging has internal holes, it needs to be punched.
(5) Heat treatment
Normalizing/annealing: eliminate internal stress and improve tissue uniformity.
Tempering (quenching + tempering) : improve the strength and hardness of forgings.
(6) Finishing and inspection
Correction: removal of deformation (e.g. thermal or cold correction).
(7) Flaw detection and performance testing
Magnetic particle or ultrasonic inspection to detect surface and internal defects
Mechanical properties:
Tensile test: test standard ASTM E8 / GB/T 228.1
Impact test: Test standard ASTM E23 / GB/T 229
Jin Xiang: Analysis of composition and structure
Through the strict implementation of the above testing system, to ensure the reliability, consistency and traceability of hot die forging parts.

Forging (Die Forging) and Casting, formatted as a clear image-ready summary: